This example demonstrates sending CSV (comma separated values) data from an Arduino. We use MegunoLink’s Message Monitor to cleanly separate the CSV data from all the other messages travelling over the serial port.
Messages send to the message monitor visualizer can be written to a file using a message logger visualizer.
Separating Data from Debug
Many microcontroller boards such as the Arduino Uno offer only a single serial connection to a PC. This means all information being output to a PC has to go through the same pipe, where it all gets mixed together.
The MegunoLink Message Monitor and it’s corresponding Message class in the MegunoLink library for Arduino allow specific information to be filtered from the serial stream’s fire-hose. Each separate packet of data is wrapped inside special formatting by the Arduino library. This formatting is picked up by the Message Monitor which displays the data inside while ignoring all other serial traffic. The data can be easily copied or saved from the Message Monitor to a text file for importing into other software. You can even use different message channels to further separate messages.
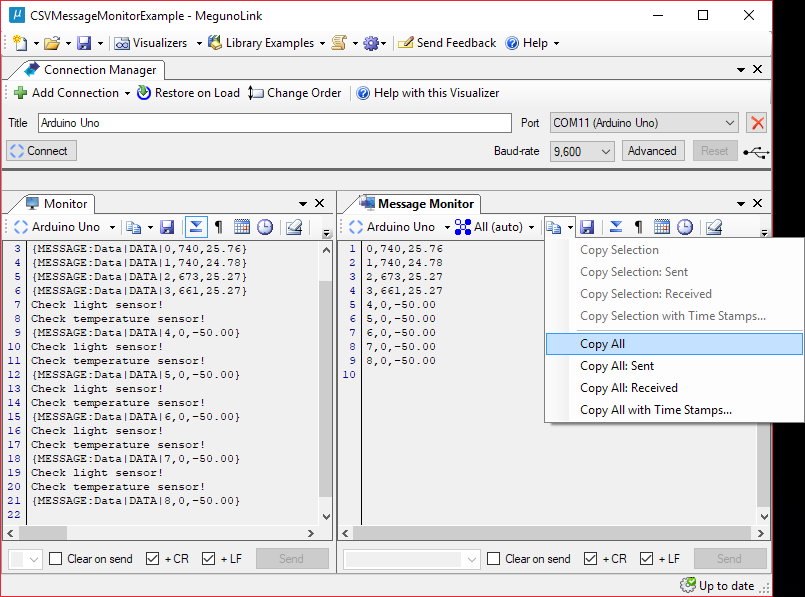
It can be hard to use measurement data sent over serial if debug statements or other non-data text are also sent. The MegunoLink Message Monitor can help by capturing only the data messages, allowing the data to be easily copied or saved.
In this example, the time and measurements of two sensors are sent over serial in Comma-Separated Value (CSV) format within Messages for the Message Monitor. These Messages were intermixed with debugging warnings sent over the same serial port. The MegunoLink Message Monitor was used to display only the CSV measurement data. From there it is easily copied to the clipboard or saved to a text file using the buttons at the top of the Message Monitor.
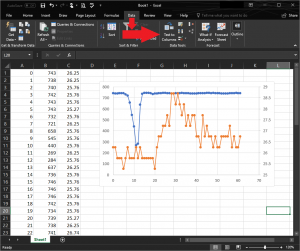
CSV-formatted values can be converted from text into proper numerical columns using Excel’s “Text to Columns” feature and selecting “Comma” as the delimiter.
The sensor data copied onto the clipboard was pasted into MS Excel and converted using the “Text to Columns” feature. It was plotted, showing the light reduction and temperature increase measured when a finger was placed on the corresponding sensor. Thus measurements over serial were easily obtained and processed without having to manually trim away debug statements or dedicating the serial port to sending only measurement data.
Additionally, the data in the messages can be nearly any string of characters you desire, not just the CSV formatted values shown here. The messages could also be received and automatically recorded to a text file by the Message Logger visualiser, without having to manually copy or save the data as with the Message Monitor.
Downloads
You can download a ZIP file containing the CSV Message Monitor example Arduino program and matching MegunoLink interface below. This example also requires our Arduino Library.
Example Code
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 |
/* *************************************************************************** * CSV Message Seperation Example * * Sends sensor measurements in Comma-Seperated Value (CSV) format * and debug mesages over serial. MegunoLink's Message Monitor visualiser * can seperate the CSV measurements from the other serial traffic, * allowing clean data recording without limiting serial usage. * * Visit https://www.megunolink.com/documentation/monitoring-data/ * to see how to use our Message Monitor and * https://www.megunolink.com/documentation/logging-data/ * to see how to use our Message Logger. * ************************************************************************* */ //--------------------Includes------------------------- // MegunoLink libraries, install if missing: //"Sketch"->"Include Library"->"Manage Libraries..."-> search and install #include "MegunoLink.h" #include "ArduinoTimer.h" //--------------------Globals------------------------- // Create Message class instance to use when sending measurement data. // "Data" = the taget message channel (select this or "All" in MegunoLink). Message MyCSVMessage("Data"); //--------------------Setup------------------------- void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); Serial.println("CSV Message Monitor Example"); Serial.print("Data format: "); Serial.println("Time[Seconds], Light[0-1023], Temperature[DegC]"); } //--------------------Loop------------------------- void loop() { // Read light measurement (photo resistor). int Light = analogRead(A0); // arbitrary ADC units (0-1023) // Check for errors in light measurement. if (Light == 0 || Light == 1023) // photo/plain resistor disconnected {Serial.println("Check light sensor!");} // Read temperature measurement (TMP36 temperature sensor). int RawTemp = analogRead(A1); // raw, unhelpful units float TempDegC = ((float)RawTemp*5*100)/1023 - 50; // Degrees C // Check for errors in temperature measurement. if (TempDegC < -10 || 40 < TempDegC) // unreasonable indoor temperatures {Serial.println("Check temperature sensor!");} // Send current time and measurement data to MegunoLink in CSV // format for recording and processing in MS Excel or MATLAB. MyCSVMessage.Begin(); Serial.print(millis()/1000); Serial.print(","); Serial.print(Light); Serial.print(","); Serial.print(TempDegC); MyCSVMessage.End(); // Wait a while, we need not rush. delay(1000); } |



